In a world drowning in data, Microsoft’s November 2023 Ignite conference unveiled a lifeline: Microsoft Fabric. This platform promises to simplify the complex data analytics landscape. But how does it deliver on that promise?
We often hear from clients curious about whether Microsoft Fabric is the right choice for their modern analytics solution. For an overview of Microsoft Fabric and its benefits as an analytics platform check out my previous article – Microsoft Fabric – A New Era for Analytics.
In chess, simplification involves strategically exchanging pieces to streamline the path to the endgame. Similarly, Microsoft Fabric has streamlined the analytics landscape, rendering many pre-November 2023 tasks obsolete.
Some new killer features in Fabric mean you no longer have to:
- Deploy infrastructure: Fabric is a complete SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solution containing all the required compute engines and storage. You don’t have to deploy any additional resources.
- Pay for, monitor, maintain and secure many disparate resources: Fabric is a single pane of glass, greatly simplifying your maintenance activities.
- Move Data: Fabric introduces the concepts of Shortcuts and OneLake, meaning many onerous ELT (extract, load and transform) tasks are a thing of the past. You remove data silos and store data once. That data is then available to all compute engines for data science, engineering, and warehousing.
- Create or refresh semantic models: Fabric includes the Direct Lake feature, a compelling new option we will explore below.
I previously wrote the blog Power BI Premium vs Azure Analysis Services that started with: “Your Power BI data model resides in one of two cloud services: Power BI, or Azure Analysis Services.”
Fabric introduces a third option of the Default Semantic Model and Direct Lake, meaning how you create and refresh models differ significantly.
Firstly, I have used the terms Data Model and Semantic Model interchangeably above. Microsoft standardised on “Semantic Model” in November 2023 to clarify the naming of Fabric entities.
This article focuses on Direct Lake, not Data Engineering, so we assume you know the Lakehouse concept. I used PySpark for Data Engineering, but you could also use Data Flows or Pipelines, depending on your preference. We ended up with a simple Sales Star schema as Delta Lake tables in our Lakehouse.
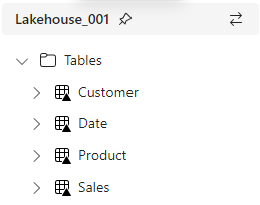
You will also see the following message:

You can query your data with SQL if you toggle to the SQL analytics endpoint.
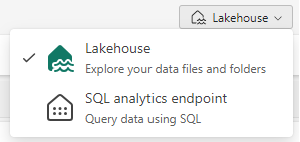
More importantly, for this article, you also have a Default Semantic Model.
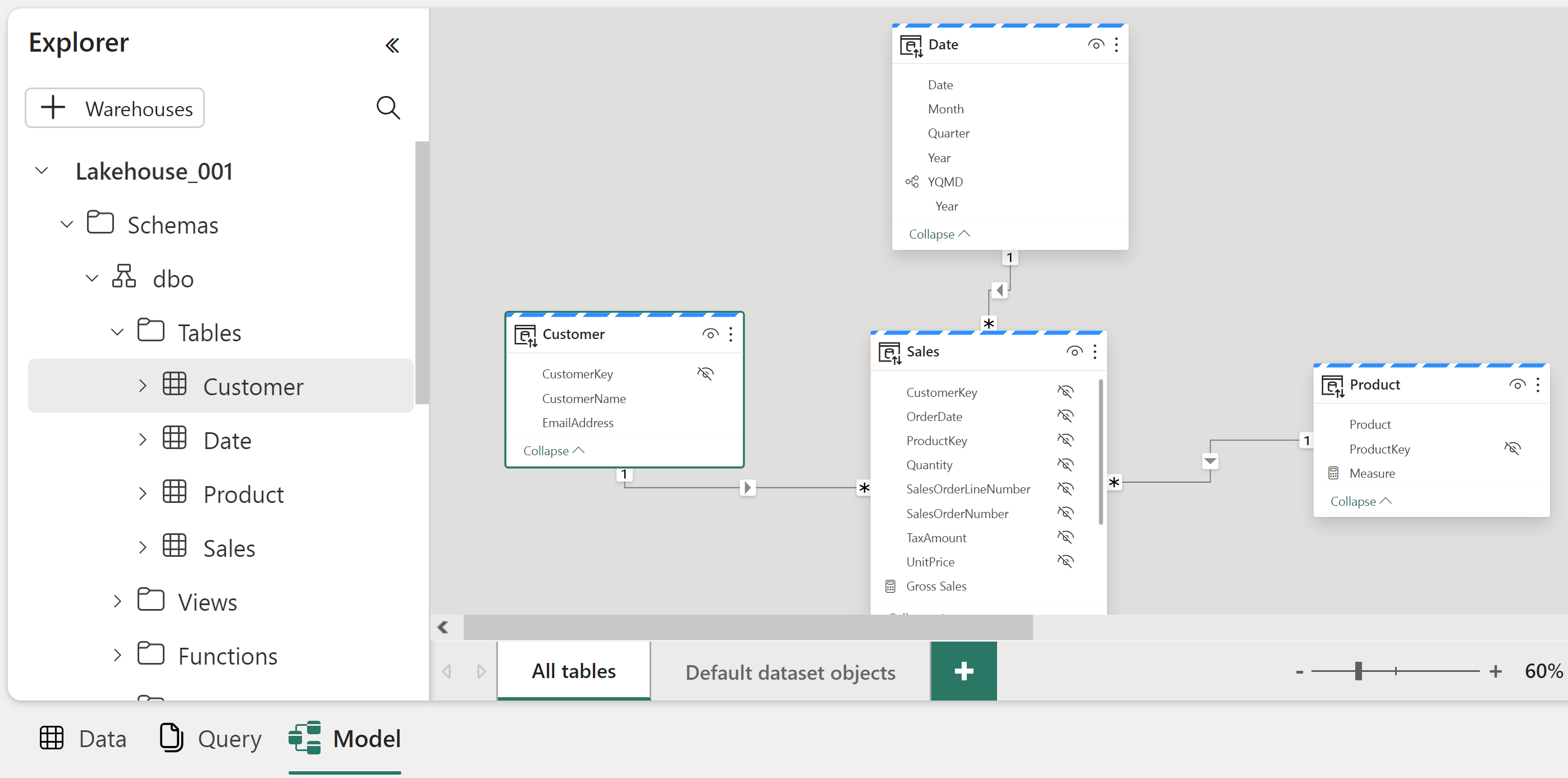
Fabric creates this model for you based on your Lakehouse with zero effort on your part. Your following action is the normal modelling activities of relating tables, formatting attributes and creating DAX measures. You can also make additional custom datasets as required.
Fabric will even automatically maintain the default Semantic Model as Direct Lake tables change.
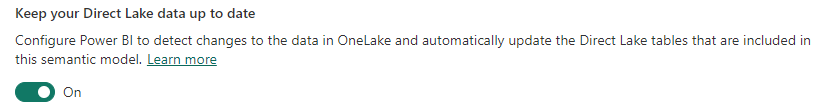
Once you have your Semantic Model, you can derive invaluable insight from your data and create reports like in my example below:
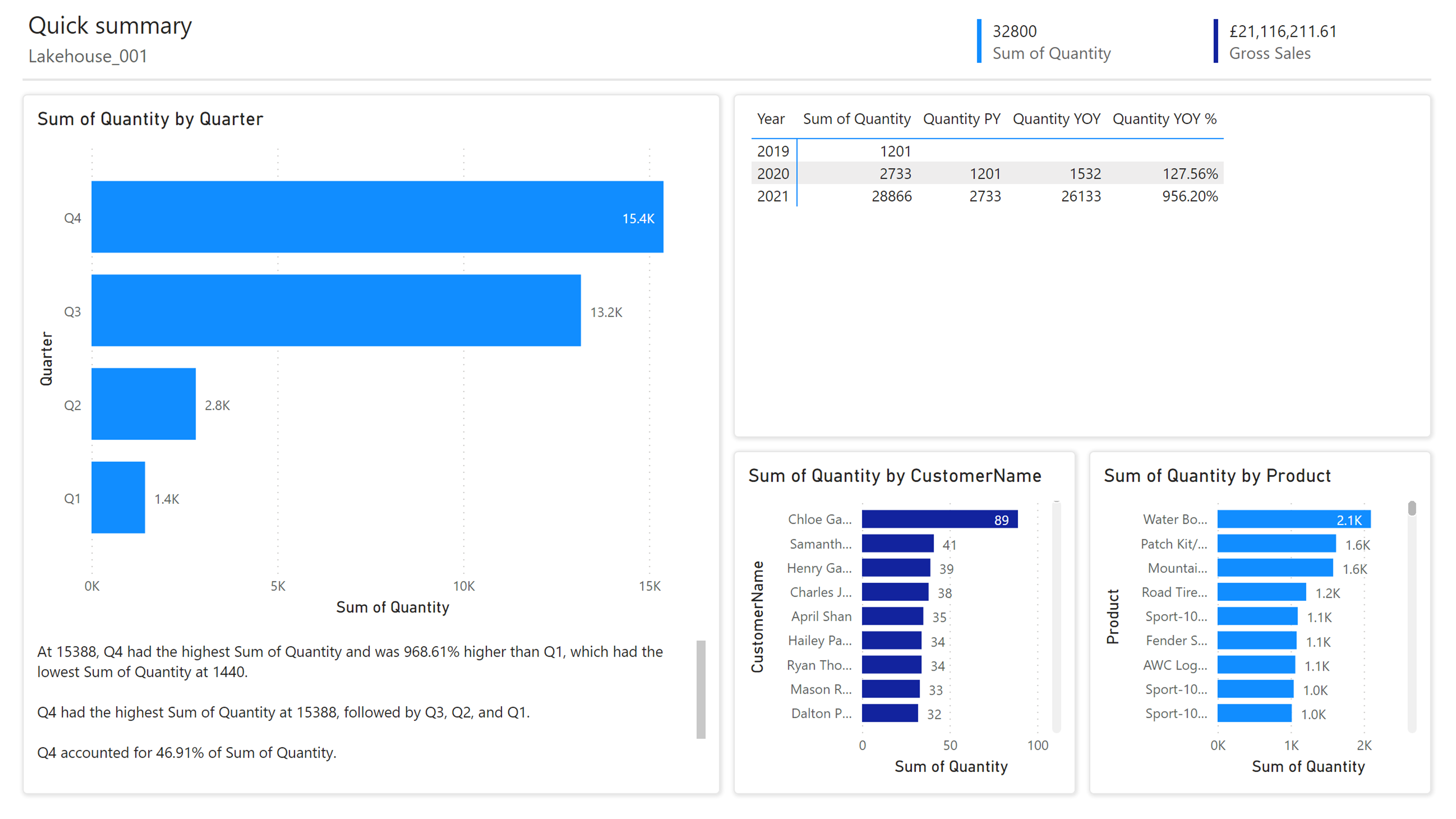
Next, I run the following Spark SQL code in my Lakehouse.

The report tile that showed 32,800 in my previous screenshot now displays 33,000. I didn’t have to perform a refresh of my dataset, and the change propagated automatically into Power BI. This feature is the true power of Direct Lake.
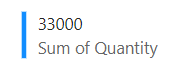
Direct Lake is a game changer for Semantic models. We get the convenience of real-time data previously achieved through Direct Query without the (sometimes severe) performance hit. Direct Lake works with Delta Lake files in your Lakehouse, which are column-based and compatible with Power BI Semantic Models for optimal performance.
Summarising the Benefits of Direct Lake:
- We no longer require additional compute between our data and Power BI such as Synapse Serverless or Databricks. Fabric handles the end-to-end data journey.
- Fabric creates the default Semantic Model for us.
- You can make additional Semantic Models that also take advantage of Direct Lake.
- Fabric maintains the Semantic Model if our Lakehouse tables change.
- Direct Lake ensures the latest data is available within your Power BI reports with no Semantic Model refresh required.
- You no longer have to make an API call to refresh your Power BI dataset after completing your ELT.
In the interests of fairness, the browser modelling experience within Fabric lacks many of the features of Power BI desktop. However, we have seen with the staggering rate of evolution of Power BI in recent years that Fabric will continually improve. As a fully-fledged cloud SaaS offering, you will automatically receive all improvements and enhancements.
What possibilities does this open for your business? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
Contact us today to explore how we can tailor Microsoft Fabric’s powerful features, including the game-changing Direct Lake, to fit your unique business needs. Our team is here to guide you through every step of the process.